Hunters -Gatherers : People who gathered their food.
Collected roots,fruits & other forest foods & Also hunted animals.Lived at the bank of river Narmada.
Sulaiman & Kirthar hills(Now in Pak) : First sign of growing crops about 8000 years ago. Beginning of rearing animals. Garo hills(North-East) & Vindhyas (Central India) were some of other areas where agriculture first developed. Rice : north of the Vindhyas.
Tributaries : Tributaries are smaller rivers that flow into a larger river.
Earliest Cities : About 4700 years ago on the banks of river Indus & its tributaries.
Later about 2500 years ago near the banks of Ganga & its tributaries, and along the sea coasts.
Ganga & its tributory Son : Area to the south of these river was know as Magadha(Bihar). Powerful Rurals, set up large Kingdom.
India & Bharat : Originated from the Indus(Sindhu in Sanskrit). Iranians & the Geeks gives the name India to the east of Indus(Hindos/the Indos) river about 2500 yrs ago.
Bharat used for people who lived north-west & are mentioned in the Rigveda(Composed in Sanskrit around 3500 yrs ago).
Manuscipts(Latin 'manu' :: hand) : Books written by hand on bark of tree called birch(Grows in Himalayas). Language used : Sanskrit,Tamil, Prakrit(version of Sanskrit used by ordinary people).
Inscriptions: Writings on hard surfaces like stones or metals. Scripts & languages are used.
Archaeology: Deals with the study of the remains of buildings made of stone & Brick, paintings and sculpture & excavate. Tools, weapons, pots, pans,ornaments & coins. Object may be made of stone, bone, baked clay or metal.
Historians : Scholars who study the past.
Source : Information found on manuscripts, inscription and archealogy.
Not Past but Pasts? Diffrent for different groups of people due to different practices , food & customs. Groups : herders and farmers, kings and queens, merchants, craft persons.
Dates : BC:: Before Christ meaning before the birth of Christianity founder Jesus Christ, counted backward.
AD :: Anno Domini(Latin) meaning in the year of the Lord or after birth of Christ.
CE :: Common Era, alternate for AD.
BCE :: Before Common Era, alternate for BC.
Decipherment : Process of understanding usuallly the inscriptions. Egypt, country in the north America, in which to the north coast town Rosetta inscripts in three different languages(Greek & two forms of Egyptian) were found. Lion stood for L, bird for A.
-------
Movements of Hunter-gatherers : Reasons -
i) Eaten up all the food of one place.
ii) Follow the animal's movements.
iii)Seasonal movements due seasonal fruit bearing characterstics of plants & trees.
iv)Need of water in dry season.
Sites : Are places where the remains of things (e.g. tools, pots, buildings) were found.
Factory: Stones & people made tools sites.
Habitation-cum-factory : People lived for long time & made tools.
Making stone tools:
i) Stone on stone : Core held in one hand & hammer held by second to strike off flakes from the first. Core turned into tool.
ii) Pressure flaking: Core was place on firm surface and hammer on a piece of bone or stone was used to apply pressure.
Fire: Kurnool caves:: traces of ash.
Change in Environment: Around 12,000 yrs ago, a shift to relatively warm conditions led to the development of grasslands. This led to increase in the number of animals.People learned about animals food habits & breeding seasons, Fishing. Development of grain bearing grasses : wheat, barley, rice etc. in the subcontinent.
Names & Dates:
Palaeolithic(Greek, 'palaeo' :: old, 'lithos' :: stone) : Points to the importace of finds of stone tools. Extends from 2 million years ago to 12,000 years ago. Divided into the Lower, Middle & Upper Palaeolithic. This covers 99% of human history. Sites : Hunsgi<many sites> most tools were made from limestone. France: Paintings(made 20,000-10,000 yrs ago) of wild animals. Colours from minerals like ochre or iron ore, and charcoal.
Collected roots,fruits & other forest foods & Also hunted animals.Lived at the bank of river Narmada.
Sulaiman & Kirthar hills(Now in Pak) : First sign of growing crops about 8000 years ago. Beginning of rearing animals. Garo hills(North-East) & Vindhyas (Central India) were some of other areas where agriculture first developed. Rice : north of the Vindhyas.
Tributaries : Tributaries are smaller rivers that flow into a larger river.
Earliest Cities : About 4700 years ago on the banks of river Indus & its tributaries.
Later about 2500 years ago near the banks of Ganga & its tributaries, and along the sea coasts.
Ganga & its tributory Son : Area to the south of these river was know as Magadha(Bihar). Powerful Rurals, set up large Kingdom.
India & Bharat : Originated from the Indus(Sindhu in Sanskrit). Iranians & the Geeks gives the name India to the east of Indus(Hindos/the Indos) river about 2500 yrs ago.
Bharat used for people who lived north-west & are mentioned in the Rigveda(Composed in Sanskrit around 3500 yrs ago).
Manuscipts(Latin 'manu' :: hand) : Books written by hand on bark of tree called birch(Grows in Himalayas). Language used : Sanskrit,Tamil, Prakrit(version of Sanskrit used by ordinary people).
Inscriptions: Writings on hard surfaces like stones or metals. Scripts & languages are used.
Archaeology: Deals with the study of the remains of buildings made of stone & Brick, paintings and sculpture & excavate. Tools, weapons, pots, pans,ornaments & coins. Object may be made of stone, bone, baked clay or metal.
Historians : Scholars who study the past.
Source : Information found on manuscripts, inscription and archealogy.
Not Past but Pasts? Diffrent for different groups of people due to different practices , food & customs. Groups : herders and farmers, kings and queens, merchants, craft persons.
Dates : BC:: Before Christ meaning before the birth of Christianity founder Jesus Christ, counted backward.
AD :: Anno Domini(Latin) meaning in the year of the Lord or after birth of Christ.
CE :: Common Era, alternate for AD.
BCE :: Before Common Era, alternate for BC.
Decipherment : Process of understanding usuallly the inscriptions. Egypt, country in the north America, in which to the north coast town Rosetta inscripts in three different languages(Greek & two forms of Egyptian) were found. Lion stood for L, bird for A.
-------
Movements of Hunter-gatherers : Reasons -
i) Eaten up all the food of one place.
ii) Follow the animal's movements.
iii)Seasonal movements due seasonal fruit bearing characterstics of plants & trees.
iv)Need of water in dry season.
Sites : Are places where the remains of things (e.g. tools, pots, buildings) were found.
Factory: Stones & people made tools sites.
Habitation-cum-factory : People lived for long time & made tools.
Making stone tools:
i) Stone on stone : Core held in one hand & hammer held by second to strike off flakes from the first. Core turned into tool.
ii) Pressure flaking: Core was place on firm surface and hammer on a piece of bone or stone was used to apply pressure.
Fire: Kurnool caves:: traces of ash.
Change in Environment: Around 12,000 yrs ago, a shift to relatively warm conditions led to the development of grasslands. This led to increase in the number of animals.People learned about animals food habits & breeding seasons, Fishing. Development of grain bearing grasses : wheat, barley, rice etc. in the subcontinent.
Names & Dates:
Palaeolithic(Greek, 'palaeo' :: old, 'lithos' :: stone) : Points to the importace of finds of stone tools. Extends from 2 million years ago to 12,000 years ago. Divided into the Lower, Middle & Upper Palaeolithic. This covers 99% of human history. Sites : Hunsgi<many sites> most tools were made from limestone. France: Paintings(made 20,000-10,000 yrs ago) of wild animals. Colours from minerals like ochre or iron ore, and charcoal.
Mesolithic(middle stone) : 12,000 yrs ago till about 10,000 yrs ago. Environmental change. Stone tools called "microliths" means tiny tools. Tools Saws, Sickles.
Neolithic : From about 10,000 yrs ago.
Rock paintings : Found in many caves specially in MP & Southern UP. Wild animals,people with great accuracy.
Ostriches in India: Found in Palaeolithic period.Ostrich egg shells were found in Patne Maharashtra, designs, beads were made.
---------
Varieties of Foods : Different crops and animals prefer different environment hence grown/ reared on this basis. Rice need more water than wheat and barley. Sheep & goat can survive in dry area than cattles.
Domestications : Gradual Process in which people grow plants and look after animals.Selection of plants & animals for domestication i.e. wheat, barley and sheep, goat. Began about 12,000 yrs ago.
Storing the food : Grains : large clay pots or wove baskets or pits into the ground.
Animals : reared them :).
First Farmers & herders: Evidence of plants(remains of burnt grain) & animal bones. Sites: Mehrgarh, Burzahom, Chirand, Koldihwa,Mahagara, Daojali Hading,Paiyampalli,Hallur etc.
Fig: Earlier crops & their places
Settlements/ Villages : Traces of huts & houses.Most people are engaged in food production.
Pithouse(underground houses, steps leading into them) in Burzahom. Cooking hearths both insides & outside of the huts. Tools(Neolithic) : with fine cutting edges and mortars & pestles for grinding grain, earthen pots(for storing/cooking food) sometimes decorated, weaving of clothes: cotton & others.Hunting-gathering continued so as the palaeolithic tools.
Mehrgarh: One of the places where barley & wheat were first grown and reared sheep & goats are first reared. Animals bones(deer and pig etc) at earliest level while excavation. Later level: bones of sheep & goat, still later level cattle bones. Remains of square or rectangular houses, four or more compartments each, probably used for storage. Burial sites with goats.Cotton(7000 yrs ago)
Daojali Hading: Located on the hills near the Brahmaputra valley. Stone tools : including mortars and pestles, jedeite: a stone probably brought from China,tools made of fossil wood , pottery.
Turkey: Most famous Neolithic site. Findings of Catal Huyuk, things brought from distance are flint(Syria),cowries(Red Sea),shells(Miditerranean Sea) used in settlement. No carts, things were carried on the back of animals or by people.
Tribes : Farmer & herders lived in groups called tribe. Two to three generations, families related to one another. Leaders: Old & Experieced or young warriors or priests. Old woman : Wisdom and Experience. Rice & unique cultural traditions: Language, music,stories & paintings, their own gods and goddesses.
---------
Earliest Cities
Harappa : All cities that have similar buildings and other things were found were described as Harappan.Developed about 4700 yrs ago, found nearly 150 yrs ago while railway lines were being laid down in Punjab but ignored. About eighty yrs ago archaeologists found the site.
Specialities of these cities: Cities were divided into two or more parts.
Citadel : part to the west, smaller but higher..
Lower town: part to the east, larger but lower.
Walls of baked bricks laid in an interlocking pattern.
Special buildings on the citadels: tank(The Great Bath) in Mohenjodaro made of bricks, coated with plaster & natural tar to make it water-tight, steps leading into the tank, tank sorrounded by the rooms. Copper objects are also found at this site.
Fire altars : At Kalibangan & Lothal, probably for sacrifice performance.
Elaborate store houses : Mohenjodaro, Harappa and Lothal.
Houses : One or two sroreys high, with rooms built around a courtyard.
Covered drains: Many of the cities, drain had a gentle slope, houses were connected to those on streets,smaller drains led into bigger ones. Houses,drain & street.
Rulers: Planned the construction of special buildings in the city. Send people to collect valuable stones & other things.
Scribes : People who knew how to write, who helped prepare the seals and on other materials.
Craft-person : Who made all kinds of things either in their homes or in special workshops. Terracotta toys.
Things made of stone, shells and metal including copper, bronze, gold and silver are found. Copper and bronze were used to make tools, weapons, ornaments and vessels. Gold and silver were used to make ornaments and vessels. Weights,beautiful black designed pots, beads ,blades and seals(generally rectangular with an animal carved on them).
Faience : A material that is artificially produced used to make beads, bangles, earrings and tiny vessels. A gum was used to shape sand or powdered quartz into an object. The objects were then glazed, resulting in a shiny, glassy surface. The colours of the glaze were usually blue or sea green.
Specialist: Person who trained to do one kind of work. For example, cutting stone, polishing beads or carving seals.
Importing by Harappans : Copper(Rajasthan Or Oman in West Asia),Tin(Afganistan & Iran),Gold(Karnataka), precious stones(Gujrat, Iran & Afganistan).
Use of carter(found toy carters). Use of Plough(toy model): to dig the earth for turning the soil and planting seeds. Some form of irrigation.
Harappan towns in Gujrat :
Dholavira : Located on Khadir Beyt in Rann of Kutch, Fresh water and fertile soil. Divided into three parts, each was sorrounded with massive walls with entrance gateways. Large open area for public ceremonies. Large letters of the Harappan scripts carved out of white stone & perhaps inlaid in wood. This was unique since usually Harappan writings found on small objects such as seals.
Lothal : Close to Gulf of Khambat beside a tributary of the Sabarmati. Raw materials such as semi-precious stones. Centre for making objects out of stone, shell & metal. A store house in the city. Seal & sealings(impression on clay),a dockyard, workshop for making beads.
Around 3900 years ago people stop living in many of these cities for unknown reason.
---------
The Vedas : Composed about 3500 yrs ago(Printed less than 200 yrs ago).More than thousand hymns, praise of various gods & goddesses. Agni: God of fire, Indra: A warrior god, Soma: a plant from which a special drink was prepared.
Four Vedas: the Rigveda(oldest & in Vedic Sanskrit), Samaveda,Yajurveda & Atharvaveda.
Family of Languages: Originally different languages have words in common.
Indo-European : Assamese, Gujarati, Hindi, Kashmiri , Sindhi(Indian) & Persian(Asian), English, French, German,Greek,Italian & Spanish(European).
Tibeto-Burman : Tamil,Telugu, Kannada
Dravidian family : Malayalam
Austro-Asiatic : Languages spoken in Jharkhand & in parts of central India.
What we find in the Rigveda: Composed in north-west of the subcontinent.
Prayers for cattle, children(Specially sons) & horses(were yoked to chariots). Battles for land(important for pasture,hardy crops), for water and to capture people.Wealth obtained was kept by leaders, some to priests & rest to people, some wealth was used to perform yajnas(sacrifices). No regular army(most men only) but assemblies to discuss matters of war and selection of leader.
Groups of people based on the work they do, language, place. family, communities & culture practices. Based on work : i) Brahmins :: Who performs various rituals, ii) Rajas:: Not like the one with capital cities, palaces or armies nor did they collected taxes, Son did not automatically succeed fathers as rajas.
Two words to describe people as a whole : jana & vish(or vaishya). For example pura jana or pura vish, the Yadu jana or vish etc.
Aryas : Who composed the hymns & called their opponents Dasas or Dasyus. Later the term dasa(faminine dasi) meant for slave.
Megaliths(Literally big stones): carefully arranged by people to mark the burial sites(On the surface or underground). Dead were buried with distinctive pots(Black & Red Ware), with weapon of iron, sometimes skeletons of horses, horse equipment and ornaments of stone & gold . Practice of erecting megaliths began about 3000 yrs ago, was prevalent throughout the Deccan, south India, north-east and Kashmir. Some megaliths contain more than one skeletons(might be belonging to same family), brought together via portholes.
Social differences : Brahmagiri: one skeleton was buried with 33 gold beads, 2 stones beads, 4 copper bangles and one conch shell(Might be rich). Other skeletons have only a few pots(poor).
Inamgaon: Site on the river Ghod(tributary of Bhima), occupied between 3600 and 2700 years ago. Adults were buried underground, laid out straight, head towards the north.Some burials within the houses. Houses had granary. Seeds of wheat, barley, rice , pulses, millets, peas and sesame. Bone of cattle, buffalo,, goat, sheep, dog, horse,ass, pig, sambhar, spotted deer, blackbuck,antelop,hare and mangose. Birds, crocodile, turtle, crab and fish. Fruits : ber , amla, jamun, dates and variety of berries.
Charaka : Wrote Charaka Samhita(about 2000 yrs ago), proposed 360 bones in human body in contrast to 200 bones in modern anatomy. Probably counted teeth, joints and cartilage.
China : First evidence of writings around 3500 yrs ago on animal bones(oracle bones) used to predict the future.
--------
Kings & Kindom
Around 3000 yrs changes in the ways in which rajas were chosen before that they were probably chosen by janas. Ashvamedha or horse sacrifice, rajas had a special seat, a throne or a tiger skin. Charioteer, companion of raja in the battle field, witness and chanted tales of his glory. Wives and sons performed variety of minor rituals. Other rajas were spectators. Priests performed rituals like sprinkling of the sacred water. Ordinary people vish bought gifts. Shudras were not allowed to attend such rituals.
Varnas: Later Vedic (Samaveda, Yajurveda, Atharvaveda and other books) composed in the north India, near Ganga & Yamuna. Later Vedic because these books were composed after the Rigveda. They contained rules about society.
Priests divided people in four groups(on the basis of birth or work) called Vernas. Each verna has a different set of functions.
i) Brahmins : Study & teach the Vedas, perform sacrifices and receive gifts.
ii) Kshatriyas : Rulers, expected to fight battles and protect the people.
iii) Vaishyas(Vish): farmers, herders and traders.
iv) Shudras : served other three groups,not allowed to study, could not perform any rituals.Women were also considered as shudras.
Both Brahmins & Kshatriyas could perform rituals.Many didn't accept the system of varna.
Untouchable : Some crafts-person, hunter-gatherers, people how helped to perform burials and cremations.
Janapadas : The word janapadas literally means the land where the jana set its foot, and settled down. Rajas of janapadas rather than janas. Settlements such as Purana Qila in Delhi, Hastinapura near Marut and Atranjikhera near Etah( last two are in UP). Huts, cattles and other animals, grew crops.
Mahajanapadas(Important janapadas): About 2500 yrs ago, had fortified capital city. Forts, large buildings, walls were built to protect people from attacks or to show richness and power of rajas, also people could be control easily. Mantained paid( punch maked coins) armies, collected taxes as 1/6th(known as bhaga or share) from farmers, work for some day from crafts-person,from herders in the form of animals & animal produce, taxes on goods bought or sold though trade. Change in agriculture such as use of iron ploughshares, transplantation of paddy.Slaves(dasas & dasis) and landless agricultural labourers known as kammakaras.
Fig : Important Janapadas
Magadha : Most imp mahajanapada in about two hundred years, Capital:first Rajagriha(Bihar) then shifted to Pataliputra(Patna). Ganga & Son(transport,water supplies, making land fertile) flowed through it, Forests.Elephants captured and trained for the army.Iron mines. Powerful rulers Bimbisara and Ajatasattu, tried to conquer other janapadas. Mahapadma :another imp ruler, extended control up to north-west. Alexander(2300 yrs ago) ruler of Macedonia in Europe, wanted to conquer the world,conquer parts of Egypt & West Asia but in Indian subcontinent reached up to the bank of river Beas but return due to fear among army of Indian ruler and their army.
Vajji : Capital Vaishali(Bihar), gana or sangha : different form of government with many rulers, sometimes with thousands of men ruled together, each was known as raja. raja perfomed rituals together. Assemblies for discussion and debate, dasas & kammakaras excluded from assemblies.Lasted for a long time till about 1500 yrs ago when ganas were conquered by Gupta rulers.
Buddha & Mahavira belong to ganas or sanghas. Digha Nikaya famous Buddist book written down about 2300 yrs ago. Ajatasattu wanted to attack the Vajjis. Chaityas : local shrines.
Greece and Athens : around 2500 yrs ago, Athensian set up democracy, all men over 30 were recognized as full citizens(Women,foreigners,several thousands of slaves worked in mines, fields were not considered as citizens). There was an assembly that met at least 40 times a yr for imp matters.All citizens could attend these meetings. Appointment for many positions were made through lottery.
--------
The story of the Buddha
Siddhartha(Gautama) , the founder of Buddhism was born about 2500 yrs ago.Buddha or the Wise One belonged to Sakya gana & was a kshatriya, it was a period of rapid changes.Left home in a young age, wandered for several yrs, meeting & holding discussions with other thinkers. Finally decided to find his own path to realisation, and meditated for days on end under a peepal tree at Bodh Gaya(Bihar) where he attained enlighment. Went to Sarnath, near Varanasi where he tought for the first time. Spend life travelling on foot, teaching(in Prakrit) till he passed away a Kusinara.
"Life is full of suffering and unhappiness because we have cravings and desires."- Buddha
Upanishads(Literally means 'Approaching and sitting near'): Around the time of Buddha or even before other thinkers(mostly men exception like Gargi a woman) tried to find answers to difficult questions.Felt that something is permanent in the universe even after death, described this phenomenon as atman or the individual soul and the brahman or the universal soul . Believed that ultimately, both the atman and the brahman were one. Many of their ideas were recorded in the Upanishads.Texts contain conversation between teachers and students, ideas were presented through simple dialogues. Poor rarely took part in these discussions, exception Satyakama Jabala(best known thinker of the time) named after his mother, the slave woman Jabali was accepted as a student by a brahmin teacher named Gautama.Upanishads were later developed by the famous thinker Shankaracharya.
Panini: The man who prepared grammer for Sanskrit, arranged the vowels and the consonants in a special order and then used these to create Algebra like formula, used these to write down the rules of the language in short formulae(around 3000 of them!).
Jainism : Around 2500 yrs ago(same period as of Buddha), the last and 24th tirthankara of the Jainas, Vardhamana Mahavira(Kshatriya prince of Lichchhavis, a grp that was part of the Vajji sangha) spread his message in Parkrit. Left home at thirty, hard and lonely life for twelve yrs at the end he attained enlightenment. Followers of Mahavira known as Jainas(Come from the word Jina meaning conqueror) lead simple lives, begging for food(hence known as bhikkhus / bhikkhunis, Prakrit word), absolutely honest and specially asked not to steal, had to observe celibacy, men had to give up everything, including their clothes. Jainism supported mainly by traders. Over hundred years it spread over north India, to Gujrat, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka. Teachings were written down and preserved at a place called Valabhi in Gujrat(aobut 1500 yrs ago).
"Men and Women who wished to know the truth must leave their homes. They must follow very strictly the rules of ahimsa which means not hurting or killing living beings."
"All beings, long to live. To all things life is dear." - Mahavira
The sangha : Association of those who left their homes. Vinaya Pitaka(a book) contains the rules for the Buddhiest sangha .
Monasteries : Supporters built temporary shelters or they lived in natural caves in hilly areas. Monk and nun felt the need of permanent shelters known as viharas or monasteries. Earliest made of wood then of bricks, some were in caves specially in western India.
The system of Ashramas : Developed by brahmins. Ashrama does not mean a place where people live and meditate but for a stage of life. Four ashramas.
i) Brahmacharya : lead simple lives and study the Vedas during the early yrs of their life.
ii) Grihastha : marry and live as householders
iii)Vanaprastha : live in the forest and meditate
iv) Samnyasa : give up everything and become samnyasins.
The system of ashramas allowed men to spend some part of their lives in meditation. Generally, women were not allowed to study the Vedas, and they had to follow the ashramas chosen by their husbands.
Iran : Zoroaster , an Iranian prophet. His teachings are contained in a book called the Avesta or Zend Avesta(language and practices described in it are very similar to those of Vedas). Zoroastrianism lasted more than a thousand yrs. Some migrated from Iran and settled down in the coastal towns of Gujrat and Maharashtra, they were the ancestors of todays' Parsis.
“Lord, grant strength and the rule of truth and
good thinking, by means of which one shall create
peace and tranquillity.”
"Good thoughts, Good words, Good Deeds"
-------
Ashoka
Big kingdom = an empire
Ashoka was one of the greatest rulers,instructions inscribed on pillars, rock surfaces.Empire was founded by his grand father Chandragupta Maurya(supported by Chanakya or Kautilya) more than 2300 yrs ago. Many cities in the empire including capital Pataliputra, Taxila and Ujjain. Different languages, food & clothes(spinning and weaving, since rules for the same are found in Arthashatra) at different parts of the empire.
Ruling the Empire : Area around Pataliputra was under direct control of the emperor. Paid Officials for the collection of taxes, spies kept a watch on the officials. Other area ruled by provincial capital such as Taxila or Ujjain. Some amount of control from Pataliputra, and royal princes were sent as governers, local customs and rules. Mauryas tried to control roads and rivers to collect tax and tribute.North-west : blankets, south India: Gold and precious stones according to the Arthashastra. People living in forest were more or less independent.
Arthashastra: Collection of Chanakya's idea.
Dynasty: When members of the family become rulers one after another, the family is called a dynasty. Mauryas dynasty: Chandragupta, his son Bindusara , his son Ashoka.
Tribute : Unlike the taxes which were collected on the regular basis, tribute was collected as and when it was possible from people more or less willingly.
Contemporary Greek ruler of West Asia named Seleucus Nicator once send his ambassador named Megasthenes to the court of Chandragupta. He described Patalipura as large andd beautiful city with 570 towers and 64 gates, multi-storeys houses made of wood and mud brick, king palace is also made of wood and decorated with stone carvings.
Ashoka: A unique ruler
Most famous ruler who tried to take his messages to the people through inscriptions(Prakrit written in Brahmi script).
War in Kalinga(ancient name of coastal Orissa): Ashoka fought a war eight years after becoming king to conquer Kalinga afterwards he was so horrified when saw the voilence and bloodshed that he decided not to fight any more wars. Only king in the history who gave up conquest after winning a war. He believe that winning people over through dhamma(Prakrit word for the Sanskrit term 'Dharma') is much better than conquering them through force.
Dhamma: Ashoka's dhamma did not involve warship of god, performance of sacrifices. He inspired teachings of Buddha. Appointed officials(dhamma mahamatta) to teach people about dhamma in empire as well as Syria,Egypt, Greece and Sri Lanka. Built roads,wells, rest houses, arranged for medical treatment for human beings and animals.
"Being gentle with slaves and servants.
Respecting one’s elders.
Treating all creatures with compassion.
Giving gifts to brahmins and monks.”
“It is both wrong to praise one’s own religion or criticise another’s."
Emperors in China began building the Great Wall somewhat before the time of Mauryan empire about 2400 yrs ago. It was meant to protected the northern frontier of the empire from pastoral. The wall is about 6400 km long, and is made of stone and brick, with a road along the top.There
are watch towers all along, at distances of about 100-200 m.
-------
Vital Villages, thriving Towns
Use of iron around 3000 yrs ago. largest collection of tools and weapons were found in megalithics burials. Growing use of iron tools(axes, ploughshare,sickle, tongs) around 2500 yrs ago. Irrigation works like canals, wells, tanks, artificial lakes during this period of time.
People in Villages: Mostly three diffrent kinds in the sourthen and northern parts.
In Tamil region: vellalar:: Large landowners. uzhavar:: Ordinary ploughmen. kadaisiyar and adimai:: landless labourers including slaves.
In northern part: grama bhojaka:: village headman usually large landowners, post was hereditary. Sometimes functions as a judge or policeman. grihapatis:: Smaller landowners. dasa karmakara:: landless labourers.
Sangam: Earliest work in Tamil, called Sangam due to compilation in the assemblies(known as sangams) of poets that were held in the city of Madurai. Above Tamil terms are mentioned in Sangam.
Jatakas: Stories composed by ordinary people, written down and preserved by Buddhist monks.
Ring wells: In many cities, archaeologists have found rows of pots, or ceramic rings arranged one on top of the other. These are known as ring wells. Used as toilets, drains and garbage dumps. Findings of the earlier cities can be done by archaeologists as well as by the accounts of the sailors and that of travellers.
Bharuch (Barygaza in Greek): Imports into Bharuch: wine, copper, tin, lead, coral, topaz,cloth, gold and silver coins.
Exports from Bharuch : plants from the Himalayas, ivory, agate, carnelian, cotton, silk and perfumes. Special gifts by the merchants to the kings like woman, singing boys, fine wines and fine clothes etc.
Coins: Punch-marked coins around 500 yrs ago, generally rectangular or square, cut out of metal sheets or flattened metal globules. The coins were not inscribed, but were stamped with symbols using dies or punches.Hence, they are called punch-marked coin.
Mathura : Around 2500 yrs ago, was important becouse located at the cross of two major routes- from the northwest to the east and from the north to south.Fortifications, several shrines, extremely fine sculpture. Around 2000 yrs ago, Mathura became the second capital of the Kushanas. religious centre: Buddhist monasteries, Jaina shrines, imp centre for the worship of Krishna. Inscriptions on surfaces of stone slabs and statues mention goldsmiths, blacksmiths, weavers, basket makers, garland makers, perfumers.
Northern Black Polished Ware(NBPW) : Generally found in the northern part of the subcontinent.NBPW is a hard, wheel made, metallic looking ware with a shiny black surface. The
potter used to expose the earthenware to very high temperature in his kiln which resulted in the blackening of its outer surface. Fine black slip was applied to give it mirror-like shine.
Shrenis: Associations of crafts-person and merchants.Shrenis provided training, procured raw material and distributed the finished product.Shrenis organized the trade, served as banks.
Arikamedu(b/w 2200 and 1900 yrs ago) : Coastal settlement, ships unloaded goods from distant lands. Brick structure probably a warehouse, pottery for the Mediterranean region such as amphorae(tall double-handed jars) , stamped red-glazed pottery known as Arretine Ware, which was named after a city in Italy. Beads from semi-precious stones and glass.
Rome : One of the oldest city in Europe, capital of one of the largest empires which spread across Europe, North Africa, and West Asia. Augustus : most imp emperors ruled about 2000 yrs ago said he found a city of brick, and made it into a city of marble. built temples,palaces, amphitheaters: open arenas surrounded by tiers of seats.
-------
Traders, Kings and Pilgrims
South India : Famous for gold, spices, epicially pepper(Known as black gold,valued in the Roman Empire), precious stones.Roman gold coins in south India. Traders explored sea routes, followed the coasts, the Arabian Sea & Bay of Bengal, took advantage of monsoon winds.
Muvendar(Tamil word from Sangam) : Three chiefs heads of three rulings families(around 2300 yrs ago), the Cholas, Cheras & Pandyas. Each of three chiefs had two centres of power: One inland, and one on the coasts. imp among these 6 cities were Puhar(Kaveripattinam): the port of the Cholas, Madurai: the capital of the Pandyas. no regular taxes but demanded gifts, military expeditions, tributes from neighbouring areas.kept some wealth and distributed the rest.
Satavahanas dynasty : Imp ruler were Gautamiputra Shri Satakarni(known through inscription on behalf of his mother Gautami Balashri). Lords of the Dakshinapatha(route leading to the south/ name for south region): he & other Satavahana rulers
Silk and Silk Route:
Silk : smooth texture-> highly valuable fabric. Making is complicated, raw silk from cocoons of silk worms, spun into thread and then woven into clothes. Invented in China around 7000 yrs ago, kept secret for thousands of years, around 2000 yrs ago became the fashion among the rich, trader from China carried silk with them, path followed by them is known as Silk Route.
Kushanas: Best known Silk Route controllers(Kanishka::famous Kuhshana ruler),ruled over central Asia and north-west India, 2000 yrs ago, major center of power: Peshawar, Mathura. Taxila was part of their kingdom,earliest ruler who issued gold coins.During their rule, a branch of the Silk Route extended from Central Asia down to the seaports at the mouth of the river Indus, from where silk was shipped westwards to the Roman Empire.Kanishka organised Buddhist councils,Ashvagosha (a poet) composed a biography of Buddha, the Buddhacharita, lived in Kanishka's court.New form of Buddhism known as Mahayana Buddhism developed(features: rather than sculpture of the Buddha's presence, now statues of the Buddha were made, second change was belief in Bodhisattvas: persons who had attained enlightment).Bodhisattvas became popular, spread throughout Central Asia, Korea and Japan, west and south of India.Theravada Buddhism(Older form of Buddhism): south eastwards such as Shri Lanka, Myanmar, Thailand, Indonesia.Dozens of caves for monks located near Western Ghats.
Pilgrims: are men and women who undertake journeys to holy places in order to offer worship.
Chinese Buddhist pilgrims : Fa Xian(1600 yrs ago), Xuan Zang(1400 yrs ago), I-Qing(50yrs after XZ), to visit Buddhist places.
Nalanda(Bihar): Famous Buddhist monastery of the period. Xaun Zang visited Nalanda.
Bhakti (bhaj meaning 'to divide or share' ): A persons' devotion to his/ her chosen diety.Hinduism, Shiva, Vishnu and goddesses such as Durga. Idea of bhakti is present in Bhagavad Gita. Emphasis on devotion and worship of a god/goddess rather than sacrifices.vAppar a devotee of Shiva. Bhakti inspired art : sculpture, poetry and architecture.
Hindu: same history as of 'India' and used to refer to people who lived to the east of the river, to their cultural practices, including religious beliefs.
Christianity: about 2000 yrs ago in West Asia, Jesus Christ born in Bethlehem part of Roman empire. Cristians of Kerala known as Syrian Cristians coz they came from West Asia, amongst the oldest Christian communitines in the world.
-------
New Empires and Kindoms
Guptas dynasty: Samudragupta: Inscription on Ashokan pillar at Allahabad,composed as Kavya by Harishena(poet and minister in the court of Samundragupta).
Prashasti : Sankrit word meaning 'in praise of', for example for Gautamiputra Shri Satakarni, Guptas etc.
Samudragupta's prashasti: warrior: A king who won victories in battle ,learned and best of poets, described as equal to gods, long sentences.Genealogies,Samudragupta's mother Kumara devi: Lichchhavi gana,his father Chandragupta: First ruler of Gupta dynasty, adopted the grand title of maharaj-adhiraja title also used by Samudragupta. Great grandfather and grandfather simply as maha-rajas.
Harishena described four different kind of rulers:
i)Rulers of Aryavarta : Nine rulers uprooted by Samdragupta and kingdom made part of empire. Green color
ii)Rulers of Dakshinapatha : twelve rulers, surrendered to Samdragupta after defeat, allowed to rule again.red dot in the map.
iii) gana sanghas, Assam, coastal Bengal, Nepal: brought tribute, followed his orders, attended his courts. Purple
iv) Rulers of outlying area perhaps descendants of the Kushanas and Shakas, rulers of Sri Lanka: Submitted to him, offered daughters in marriage. Blue
Vikram Samvat : The era beginning in the 58 BCE is traditionally associated with Gupta king,
Chandragupta II, who had founded it as a mark of victory over the Shakas and assumed the title of
Vikramaditya. The Vikram Samvat has also been adopted alongside the Gregorian calendar as the national calendar by independent India. Vikramaditya's court was full of learned people including Kalidasa(poet) & Aryabhata(astronomer).
Kalidasa : Abhijnana Shakuntalam, love story b/w a king Dushyanta & a young woman named Shakuntala.
Harshavardhana and the Harshacharita :
Known about Harshavardhana(king of Thanesar) through his biographies,ruled nearly 1400 yrs ago. Banabhatta was his court poet wrote his biography Harshacharita(genealogy of Harsha + ends with his becoming king) in Sanskrit. Xuan Zang spent a lot of time in Harsha's court. Become king after both his father's and elder brother's death.Brother-in-law was king of Kanauj killed by ruler of Bengal. Harsha took over the kingdom of Kanauj then led an army against the ruler of Bengal, was successful in the east(Magadha & Bengal) but while crossing the Narmada to march into Deccan stopped by Pulakeshin of Chalukya dynasty.
The Pallavas, Chalukyas and Pulakeshin's prashsti: The Pallavas and Chalukyas were the most
important ruling dynasties in south India during this period.
Kingdom of the Pallavas :spread around the capital Kanchipuram to the Kaveri delta.number of assemblies of brahmins land owners called sabha, sabha functions through sub-committees: looked after irrigation, agricultural operations, making roads, local temples etc.
UR: ur was village assembly of non-brahmins.
Nagaram: organisation of merchants.
Kingdom of Chalukyas: capital : Aihole(imp trading centre), centred around the Raichur Doab, b/w rivers Krishna and Tungabhadra. Pulakeshin II : best known Chalukya ruler, known by prashasti composed by his court poet Ravikirti.P-II got the kingdom from his uncle.
Pallavas and Chalukyas frequently attacked each other's kingdom. Ultimately, both dynasty gave way to new rulers of Rashtrakuta and Chola dynasties.
Administration of kingdoms: Village the basic unit of administration, to influence people some imp admin posts were made hereditary. For example, the poet Harishena was maha-danda-nayaka or chief officer, like his father. Many posts to one person, ex Harishena was also kumar-amatya(imp minister) and sandhi-vigrahika(minister of war & peace).local administration like nagara-shreshthi(chief banker), the sarthavaha(leader of merchant caravans).prathama-kulika(chief craftsman), the head of kayasthas(scribes).
New kind of army : Samantas :: no regular salaries but grants of land to collect revenue form, used this to maintain soldiers and horses, equipment for warfare. Banabhatta provide vivid picture of the kings' army.
Arabia: desert, hub of communications for centuries, Arab merchants and sailor played role in sea trade b/w India and Europe. Islam: 1400 yrs ago, introduced by a prophet Muhammad, laid stress on equality and unity of all before Allah: the one supreme god. Quran, withing 100 yrs spread over north Africa, Spain, Iran and India,Arab sailor bought new religion with them, Arab soldier conquered Sind about 1300 yrs ago.
------
The iron pillor : Mehrauli Delhi, made of iron, 7.2 m high, 3 tonnes weighs, made about 1500 yrs ago, inscription on the pillar mention ruler name Chandra(probably Gupta dynasty), not rusted in all these years.
Brick & Stone buildings : stupa :: a mound, round, tall, big & small.small box in the centre of the stupa contains bodily remains(teeth, bones or ashes) of Buddha or his followers or things used by them.Relic casket : covered with earth, later a layer of mud brick or baked brick added on top and then the dome like structure was sometimes covered with carved stone slabs. Pradakshina patha was laid around the stupa, this surrounded with railings, Amaravati: magnificent stupa about 2000 yrs ago. Other buildings were hollowed out of rock to make artificial caves, got painted walls, sculptures.
Hindu Temples : Deities such as Vishnu,Shiva, and Durga, garbhagriha: image of chief deity.sites: In Bhitargaon a tower known as shikharas(requires careful planning), mandapa: for assemblies. Others sites Mahabalipuram and Aihole: Finest stone temples
Painting : Sites : Ajanta:: several caves hollowed out of the hills, monasteries for Buddhist monks decorated with paitings: inside the cave done with in the light of torches, colours(plants & minerals) still vivid even after 1500 yrs.
Epics : grand, local compositions abt heroic men & women, stories abt gods.Tamil epic : Silappadikaram(love story of merchant name Kovalan lived in Puhar fall in love with a courtesen named Madhavi, neglected his wife Kannagi) composed by Ilango(a poet) around 1800 yrs ago. Another one Manimekalai(story of daughter of Kovalan & Madhavi) by Sattanar 1400 yrs ago. Kalidas also wrote epic(Meghaduta). Sanskrit epics the Mahabharata(written down abt 1500 yrs ago but very old, Ved Vyasa) and Ramayana(Valmiki).
Purana(old) : Written Sanskrit verse and for everyone including shudras, stories about god and goddesses such as Vishnu,Shiva,Durga or Parvati, details abt worshipping, account about the creation of the world, stories abt kings.
Jatakas & Panchatantra : Stories abt ordinary people, railings of stupas.
Books on Science : Aryabhatiyam(by mathematician & astronomer Aryabhata), Varahamihira, Brahmagupta and Bhaskaracharya. Invention of Zero, Ayurveda: Charak Samhita(Chraka abt medicine),Susruta Samhita(Sushruta abt surgical procedures)
Paper : In China abt 1900 yrs ago by Cai Lun, kept secret, reached Korea abt 1400 yrs and spread to Japan.from Baghdad(abt 1800 yrs ago) spread to Europe, Africa and other parts of Asia.
Neolithic : From about 10,000 yrs ago.
Rock paintings : Found in many caves specially in MP & Southern UP. Wild animals,people with great accuracy.
Ostriches in India: Found in Palaeolithic period.Ostrich egg shells were found in Patne Maharashtra, designs, beads were made.
---------
Varieties of Foods : Different crops and animals prefer different environment hence grown/ reared on this basis. Rice need more water than wheat and barley. Sheep & goat can survive in dry area than cattles.
Domestications : Gradual Process in which people grow plants and look after animals.Selection of plants & animals for domestication i.e. wheat, barley and sheep, goat. Began about 12,000 yrs ago.
Storing the food : Grains : large clay pots or wove baskets or pits into the ground.
Animals : reared them :).
First Farmers & herders: Evidence of plants(remains of burnt grain) & animal bones. Sites: Mehrgarh, Burzahom, Chirand, Koldihwa,Mahagara, Daojali Hading,Paiyampalli,Hallur etc.
Fig: Earlier crops & their places
Settlements/ Villages : Traces of huts & houses.Most people are engaged in food production.
Pithouse(underground houses, steps leading into them) in Burzahom. Cooking hearths both insides & outside of the huts. Tools(Neolithic) : with fine cutting edges and mortars & pestles for grinding grain, earthen pots(for storing/cooking food) sometimes decorated, weaving of clothes: cotton & others.Hunting-gathering continued so as the palaeolithic tools.
Mehrgarh: One of the places where barley & wheat were first grown and reared sheep & goats are first reared. Animals bones(deer and pig etc) at earliest level while excavation. Later level: bones of sheep & goat, still later level cattle bones. Remains of square or rectangular houses, four or more compartments each, probably used for storage. Burial sites with goats.Cotton(7000 yrs ago)
Daojali Hading: Located on the hills near the Brahmaputra valley. Stone tools : including mortars and pestles, jedeite: a stone probably brought from China,tools made of fossil wood , pottery.
Turkey: Most famous Neolithic site. Findings of Catal Huyuk, things brought from distance are flint(Syria),cowries(Red Sea),shells(Miditerranean Sea) used in settlement. No carts, things were carried on the back of animals or by people.
Tribes : Farmer & herders lived in groups called tribe. Two to three generations, families related to one another. Leaders: Old & Experieced or young warriors or priests. Old woman : Wisdom and Experience. Rice & unique cultural traditions: Language, music,stories & paintings, their own gods and goddesses.
---------
Earliest Cities
Harappa : All cities that have similar buildings and other things were found were described as Harappan.Developed about 4700 yrs ago, found nearly 150 yrs ago while railway lines were being laid down in Punjab but ignored. About eighty yrs ago archaeologists found the site.
Specialities of these cities: Cities were divided into two or more parts.
Citadel : part to the west, smaller but higher..
Lower town: part to the east, larger but lower.
Walls of baked bricks laid in an interlocking pattern.
Special buildings on the citadels: tank(The Great Bath) in Mohenjodaro made of bricks, coated with plaster & natural tar to make it water-tight, steps leading into the tank, tank sorrounded by the rooms. Copper objects are also found at this site.
Fire altars : At Kalibangan & Lothal, probably for sacrifice performance.
Elaborate store houses : Mohenjodaro, Harappa and Lothal.
Houses : One or two sroreys high, with rooms built around a courtyard.
Covered drains: Many of the cities, drain had a gentle slope, houses were connected to those on streets,smaller drains led into bigger ones. Houses,drain & street.
Rulers: Planned the construction of special buildings in the city. Send people to collect valuable stones & other things.
Scribes : People who knew how to write, who helped prepare the seals and on other materials.
Craft-person : Who made all kinds of things either in their homes or in special workshops. Terracotta toys.
Things made of stone, shells and metal including copper, bronze, gold and silver are found. Copper and bronze were used to make tools, weapons, ornaments and vessels. Gold and silver were used to make ornaments and vessels. Weights,beautiful black designed pots, beads ,blades and seals(generally rectangular with an animal carved on them).
Faience : A material that is artificially produced used to make beads, bangles, earrings and tiny vessels. A gum was used to shape sand or powdered quartz into an object. The objects were then glazed, resulting in a shiny, glassy surface. The colours of the glaze were usually blue or sea green.
Specialist: Person who trained to do one kind of work. For example, cutting stone, polishing beads or carving seals.
Importing by Harappans : Copper(Rajasthan Or Oman in West Asia),Tin(Afganistan & Iran),Gold(Karnataka), precious stones(Gujrat, Iran & Afganistan).
Use of carter(found toy carters). Use of Plough(toy model): to dig the earth for turning the soil and planting seeds. Some form of irrigation.
Harappan towns in Gujrat :
Dholavira : Located on Khadir Beyt in Rann of Kutch, Fresh water and fertile soil. Divided into three parts, each was sorrounded with massive walls with entrance gateways. Large open area for public ceremonies. Large letters of the Harappan scripts carved out of white stone & perhaps inlaid in wood. This was unique since usually Harappan writings found on small objects such as seals.
Lothal : Close to Gulf of Khambat beside a tributary of the Sabarmati. Raw materials such as semi-precious stones. Centre for making objects out of stone, shell & metal. A store house in the city. Seal & sealings(impression on clay),a dockyard, workshop for making beads.
Around 3900 years ago people stop living in many of these cities for unknown reason.
---------
The Vedas : Composed about 3500 yrs ago(Printed less than 200 yrs ago).More than thousand hymns, praise of various gods & goddesses. Agni: God of fire, Indra: A warrior god, Soma: a plant from which a special drink was prepared.
Four Vedas: the Rigveda(oldest & in Vedic Sanskrit), Samaveda,Yajurveda & Atharvaveda.
Family of Languages: Originally different languages have words in common.
Indo-European : Assamese, Gujarati, Hindi, Kashmiri , Sindhi(Indian) & Persian(Asian), English, French, German,Greek,Italian & Spanish(European).
Tibeto-Burman : Tamil,Telugu, Kannada
Dravidian family : Malayalam
Austro-Asiatic : Languages spoken in Jharkhand & in parts of central India.
What we find in the Rigveda: Composed in north-west of the subcontinent.
Prayers for cattle, children(Specially sons) & horses(were yoked to chariots). Battles for land(important for pasture,hardy crops), for water and to capture people.Wealth obtained was kept by leaders, some to priests & rest to people, some wealth was used to perform yajnas(sacrifices). No regular army(most men only) but assemblies to discuss matters of war and selection of leader.
Groups of people based on the work they do, language, place. family, communities & culture practices. Based on work : i) Brahmins :: Who performs various rituals, ii) Rajas:: Not like the one with capital cities, palaces or armies nor did they collected taxes, Son did not automatically succeed fathers as rajas.
Two words to describe people as a whole : jana & vish(or vaishya). For example pura jana or pura vish, the Yadu jana or vish etc.
Aryas : Who composed the hymns & called their opponents Dasas or Dasyus. Later the term dasa(faminine dasi) meant for slave.
Megaliths(Literally big stones): carefully arranged by people to mark the burial sites(On the surface or underground). Dead were buried with distinctive pots(Black & Red Ware), with weapon of iron, sometimes skeletons of horses, horse equipment and ornaments of stone & gold . Practice of erecting megaliths began about 3000 yrs ago, was prevalent throughout the Deccan, south India, north-east and Kashmir. Some megaliths contain more than one skeletons(might be belonging to same family), brought together via portholes.
Social differences : Brahmagiri: one skeleton was buried with 33 gold beads, 2 stones beads, 4 copper bangles and one conch shell(Might be rich). Other skeletons have only a few pots(poor).
Inamgaon: Site on the river Ghod(tributary of Bhima), occupied between 3600 and 2700 years ago. Adults were buried underground, laid out straight, head towards the north.Some burials within the houses. Houses had granary. Seeds of wheat, barley, rice , pulses, millets, peas and sesame. Bone of cattle, buffalo,, goat, sheep, dog, horse,ass, pig, sambhar, spotted deer, blackbuck,antelop,hare and mangose. Birds, crocodile, turtle, crab and fish. Fruits : ber , amla, jamun, dates and variety of berries.
Charaka : Wrote Charaka Samhita(about 2000 yrs ago), proposed 360 bones in human body in contrast to 200 bones in modern anatomy. Probably counted teeth, joints and cartilage.
China : First evidence of writings around 3500 yrs ago on animal bones(oracle bones) used to predict the future.
--------
Kings & Kindom
Around 3000 yrs changes in the ways in which rajas were chosen before that they were probably chosen by janas. Ashvamedha or horse sacrifice, rajas had a special seat, a throne or a tiger skin. Charioteer, companion of raja in the battle field, witness and chanted tales of his glory. Wives and sons performed variety of minor rituals. Other rajas were spectators. Priests performed rituals like sprinkling of the sacred water. Ordinary people vish bought gifts. Shudras were not allowed to attend such rituals.
Varnas: Later Vedic (Samaveda, Yajurveda, Atharvaveda and other books) composed in the north India, near Ganga & Yamuna. Later Vedic because these books were composed after the Rigveda. They contained rules about society.
Priests divided people in four groups(on the basis of birth or work) called Vernas. Each verna has a different set of functions.
i) Brahmins : Study & teach the Vedas, perform sacrifices and receive gifts.
ii) Kshatriyas : Rulers, expected to fight battles and protect the people.
iii) Vaishyas(Vish): farmers, herders and traders.
iv) Shudras : served other three groups,not allowed to study, could not perform any rituals.Women were also considered as shudras.
Both Brahmins & Kshatriyas could perform rituals.Many didn't accept the system of varna.
Untouchable : Some crafts-person, hunter-gatherers, people how helped to perform burials and cremations.
Janapadas : The word janapadas literally means the land where the jana set its foot, and settled down. Rajas of janapadas rather than janas. Settlements such as Purana Qila in Delhi, Hastinapura near Marut and Atranjikhera near Etah( last two are in UP). Huts, cattles and other animals, grew crops.
Mahajanapadas(Important janapadas): About 2500 yrs ago, had fortified capital city. Forts, large buildings, walls were built to protect people from attacks or to show richness and power of rajas, also people could be control easily. Mantained paid( punch maked coins) armies, collected taxes as 1/6th(known as bhaga or share) from farmers, work for some day from crafts-person,from herders in the form of animals & animal produce, taxes on goods bought or sold though trade. Change in agriculture such as use of iron ploughshares, transplantation of paddy.Slaves(dasas & dasis) and landless agricultural labourers known as kammakaras.
Fig : Important Janapadas
Magadha : Most imp mahajanapada in about two hundred years, Capital:first Rajagriha(Bihar) then shifted to Pataliputra(Patna). Ganga & Son(transport,water supplies, making land fertile) flowed through it, Forests.Elephants captured and trained for the army.Iron mines. Powerful rulers Bimbisara and Ajatasattu, tried to conquer other janapadas. Mahapadma :another imp ruler, extended control up to north-west. Alexander(2300 yrs ago) ruler of Macedonia in Europe, wanted to conquer the world,conquer parts of Egypt & West Asia but in Indian subcontinent reached up to the bank of river Beas but return due to fear among army of Indian ruler and their army.
Vajji : Capital Vaishali(Bihar), gana or sangha : different form of government with many rulers, sometimes with thousands of men ruled together, each was known as raja. raja perfomed rituals together. Assemblies for discussion and debate, dasas & kammakaras excluded from assemblies.Lasted for a long time till about 1500 yrs ago when ganas were conquered by Gupta rulers.
Buddha & Mahavira belong to ganas or sanghas. Digha Nikaya famous Buddist book written down about 2300 yrs ago. Ajatasattu wanted to attack the Vajjis. Chaityas : local shrines.
Greece and Athens : around 2500 yrs ago, Athensian set up democracy, all men over 30 were recognized as full citizens(Women,foreigners,several thousands of slaves worked in mines, fields were not considered as citizens). There was an assembly that met at least 40 times a yr for imp matters.All citizens could attend these meetings. Appointment for many positions were made through lottery.
--------
The story of the Buddha
Siddhartha(Gautama) , the founder of Buddhism was born about 2500 yrs ago.Buddha or the Wise One belonged to Sakya gana & was a kshatriya, it was a period of rapid changes.Left home in a young age, wandered for several yrs, meeting & holding discussions with other thinkers. Finally decided to find his own path to realisation, and meditated for days on end under a peepal tree at Bodh Gaya(Bihar) where he attained enlighment. Went to Sarnath, near Varanasi where he tought for the first time. Spend life travelling on foot, teaching(in Prakrit) till he passed away a Kusinara.
"Life is full of suffering and unhappiness because we have cravings and desires."- Buddha
Upanishads(Literally means 'Approaching and sitting near'): Around the time of Buddha or even before other thinkers(mostly men exception like Gargi a woman) tried to find answers to difficult questions.Felt that something is permanent in the universe even after death, described this phenomenon as atman or the individual soul and the brahman or the universal soul . Believed that ultimately, both the atman and the brahman were one. Many of their ideas were recorded in the Upanishads.Texts contain conversation between teachers and students, ideas were presented through simple dialogues. Poor rarely took part in these discussions, exception Satyakama Jabala(best known thinker of the time) named after his mother, the slave woman Jabali was accepted as a student by a brahmin teacher named Gautama.Upanishads were later developed by the famous thinker Shankaracharya.
Panini: The man who prepared grammer for Sanskrit, arranged the vowels and the consonants in a special order and then used these to create Algebra like formula, used these to write down the rules of the language in short formulae(around 3000 of them!).
Jainism : Around 2500 yrs ago(same period as of Buddha), the last and 24th tirthankara of the Jainas, Vardhamana Mahavira(Kshatriya prince of Lichchhavis, a grp that was part of the Vajji sangha) spread his message in Parkrit. Left home at thirty, hard and lonely life for twelve yrs at the end he attained enlightenment. Followers of Mahavira known as Jainas(Come from the word Jina meaning conqueror) lead simple lives, begging for food(hence known as bhikkhus / bhikkhunis, Prakrit word), absolutely honest and specially asked not to steal, had to observe celibacy, men had to give up everything, including their clothes. Jainism supported mainly by traders. Over hundred years it spread over north India, to Gujrat, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka. Teachings were written down and preserved at a place called Valabhi in Gujrat(aobut 1500 yrs ago).
"Men and Women who wished to know the truth must leave their homes. They must follow very strictly the rules of ahimsa which means not hurting or killing living beings."
"All beings, long to live. To all things life is dear." - Mahavira
The sangha : Association of those who left their homes. Vinaya Pitaka(a book) contains the rules for the Buddhiest sangha .
Monasteries : Supporters built temporary shelters or they lived in natural caves in hilly areas. Monk and nun felt the need of permanent shelters known as viharas or monasteries. Earliest made of wood then of bricks, some were in caves specially in western India.
The system of Ashramas : Developed by brahmins. Ashrama does not mean a place where people live and meditate but for a stage of life. Four ashramas.
i) Brahmacharya : lead simple lives and study the Vedas during the early yrs of their life.
ii) Grihastha : marry and live as householders
iii)Vanaprastha : live in the forest and meditate
iv) Samnyasa : give up everything and become samnyasins.
The system of ashramas allowed men to spend some part of their lives in meditation. Generally, women were not allowed to study the Vedas, and they had to follow the ashramas chosen by their husbands.
Iran : Zoroaster , an Iranian prophet. His teachings are contained in a book called the Avesta or Zend Avesta(language and practices described in it are very similar to those of Vedas). Zoroastrianism lasted more than a thousand yrs. Some migrated from Iran and settled down in the coastal towns of Gujrat and Maharashtra, they were the ancestors of todays' Parsis.
“Lord, grant strength and the rule of truth and
good thinking, by means of which one shall create
peace and tranquillity.”
"Good thoughts, Good words, Good Deeds"
-------
Ashoka
Big kingdom = an empire
Ashoka was one of the greatest rulers,instructions inscribed on pillars, rock surfaces.Empire was founded by his grand father Chandragupta Maurya(supported by Chanakya or Kautilya) more than 2300 yrs ago. Many cities in the empire including capital Pataliputra, Taxila and Ujjain. Different languages, food & clothes(spinning and weaving, since rules for the same are found in Arthashatra) at different parts of the empire.
Ruling the Empire : Area around Pataliputra was under direct control of the emperor. Paid Officials for the collection of taxes, spies kept a watch on the officials. Other area ruled by provincial capital such as Taxila or Ujjain. Some amount of control from Pataliputra, and royal princes were sent as governers, local customs and rules. Mauryas tried to control roads and rivers to collect tax and tribute.North-west : blankets, south India: Gold and precious stones according to the Arthashastra. People living in forest were more or less independent.
Arthashastra: Collection of Chanakya's idea.
Dynasty: When members of the family become rulers one after another, the family is called a dynasty. Mauryas dynasty: Chandragupta, his son Bindusara , his son Ashoka.
Tribute : Unlike the taxes which were collected on the regular basis, tribute was collected as and when it was possible from people more or less willingly.
Contemporary Greek ruler of West Asia named Seleucus Nicator once send his ambassador named Megasthenes to the court of Chandragupta. He described Patalipura as large andd beautiful city with 570 towers and 64 gates, multi-storeys houses made of wood and mud brick, king palace is also made of wood and decorated with stone carvings.
Ashoka: A unique ruler
Most famous ruler who tried to take his messages to the people through inscriptions(Prakrit written in Brahmi script).
War in Kalinga(ancient name of coastal Orissa): Ashoka fought a war eight years after becoming king to conquer Kalinga afterwards he was so horrified when saw the voilence and bloodshed that he decided not to fight any more wars. Only king in the history who gave up conquest after winning a war. He believe that winning people over through dhamma(Prakrit word for the Sanskrit term 'Dharma') is much better than conquering them through force.
Dhamma: Ashoka's dhamma did not involve warship of god, performance of sacrifices. He inspired teachings of Buddha. Appointed officials(dhamma mahamatta) to teach people about dhamma in empire as well as Syria,Egypt, Greece and Sri Lanka. Built roads,wells, rest houses, arranged for medical treatment for human beings and animals.
"Being gentle with slaves and servants.
Respecting one’s elders.
Treating all creatures with compassion.
Giving gifts to brahmins and monks.”
“It is both wrong to praise one’s own religion or criticise another’s."
Emperors in China began building the Great Wall somewhat before the time of Mauryan empire about 2400 yrs ago. It was meant to protected the northern frontier of the empire from pastoral. The wall is about 6400 km long, and is made of stone and brick, with a road along the top.There
are watch towers all along, at distances of about 100-200 m.
-------
Vital Villages, thriving Towns
Use of iron around 3000 yrs ago. largest collection of tools and weapons were found in megalithics burials. Growing use of iron tools(axes, ploughshare,sickle, tongs) around 2500 yrs ago. Irrigation works like canals, wells, tanks, artificial lakes during this period of time.
People in Villages: Mostly three diffrent kinds in the sourthen and northern parts.
In Tamil region: vellalar:: Large landowners. uzhavar:: Ordinary ploughmen. kadaisiyar and adimai:: landless labourers including slaves.
In northern part: grama bhojaka:: village headman usually large landowners, post was hereditary. Sometimes functions as a judge or policeman. grihapatis:: Smaller landowners. dasa karmakara:: landless labourers.
Sangam: Earliest work in Tamil, called Sangam due to compilation in the assemblies(known as sangams) of poets that were held in the city of Madurai. Above Tamil terms are mentioned in Sangam.
Jatakas: Stories composed by ordinary people, written down and preserved by Buddhist monks.
Ring wells: In many cities, archaeologists have found rows of pots, or ceramic rings arranged one on top of the other. These are known as ring wells. Used as toilets, drains and garbage dumps. Findings of the earlier cities can be done by archaeologists as well as by the accounts of the sailors and that of travellers.
Bharuch (Barygaza in Greek): Imports into Bharuch: wine, copper, tin, lead, coral, topaz,cloth, gold and silver coins.
Exports from Bharuch : plants from the Himalayas, ivory, agate, carnelian, cotton, silk and perfumes. Special gifts by the merchants to the kings like woman, singing boys, fine wines and fine clothes etc.
Coins: Punch-marked coins around 500 yrs ago, generally rectangular or square, cut out of metal sheets or flattened metal globules. The coins were not inscribed, but were stamped with symbols using dies or punches.Hence, they are called punch-marked coin.
Mathura : Around 2500 yrs ago, was important becouse located at the cross of two major routes- from the northwest to the east and from the north to south.Fortifications, several shrines, extremely fine sculpture. Around 2000 yrs ago, Mathura became the second capital of the Kushanas. religious centre: Buddhist monasteries, Jaina shrines, imp centre for the worship of Krishna. Inscriptions on surfaces of stone slabs and statues mention goldsmiths, blacksmiths, weavers, basket makers, garland makers, perfumers.
Northern Black Polished Ware(NBPW) : Generally found in the northern part of the subcontinent.NBPW is a hard, wheel made, metallic looking ware with a shiny black surface. The
potter used to expose the earthenware to very high temperature in his kiln which resulted in the blackening of its outer surface. Fine black slip was applied to give it mirror-like shine.
Shrenis: Associations of crafts-person and merchants.Shrenis provided training, procured raw material and distributed the finished product.Shrenis organized the trade, served as banks.
Arikamedu(b/w 2200 and 1900 yrs ago) : Coastal settlement, ships unloaded goods from distant lands. Brick structure probably a warehouse, pottery for the Mediterranean region such as amphorae(tall double-handed jars) , stamped red-glazed pottery known as Arretine Ware, which was named after a city in Italy. Beads from semi-precious stones and glass.
Rome : One of the oldest city in Europe, capital of one of the largest empires which spread across Europe, North Africa, and West Asia. Augustus : most imp emperors ruled about 2000 yrs ago said he found a city of brick, and made it into a city of marble. built temples,palaces, amphitheaters: open arenas surrounded by tiers of seats.
-------
Traders, Kings and Pilgrims
South India : Famous for gold, spices, epicially pepper(Known as black gold,valued in the Roman Empire), precious stones.Roman gold coins in south India. Traders explored sea routes, followed the coasts, the Arabian Sea & Bay of Bengal, took advantage of monsoon winds.
Muvendar(Tamil word from Sangam) : Three chiefs heads of three rulings families(around 2300 yrs ago), the Cholas, Cheras & Pandyas. Each of three chiefs had two centres of power: One inland, and one on the coasts. imp among these 6 cities were Puhar(Kaveripattinam): the port of the Cholas, Madurai: the capital of the Pandyas. no regular taxes but demanded gifts, military expeditions, tributes from neighbouring areas.kept some wealth and distributed the rest.
Satavahanas dynasty : Imp ruler were Gautamiputra Shri Satakarni(known through inscription on behalf of his mother Gautami Balashri). Lords of the Dakshinapatha(route leading to the south/ name for south region): he & other Satavahana rulers
Silk and Silk Route:
Silk : smooth texture-> highly valuable fabric. Making is complicated, raw silk from cocoons of silk worms, spun into thread and then woven into clothes. Invented in China around 7000 yrs ago, kept secret for thousands of years, around 2000 yrs ago became the fashion among the rich, trader from China carried silk with them, path followed by them is known as Silk Route.
Kushanas: Best known Silk Route controllers(Kanishka::famous Kuhshana ruler),ruled over central Asia and north-west India, 2000 yrs ago, major center of power: Peshawar, Mathura. Taxila was part of their kingdom,earliest ruler who issued gold coins.During their rule, a branch of the Silk Route extended from Central Asia down to the seaports at the mouth of the river Indus, from where silk was shipped westwards to the Roman Empire.Kanishka organised Buddhist councils,Ashvagosha (a poet) composed a biography of Buddha, the Buddhacharita, lived in Kanishka's court.New form of Buddhism known as Mahayana Buddhism developed(features: rather than sculpture of the Buddha's presence, now statues of the Buddha were made, second change was belief in Bodhisattvas: persons who had attained enlightment).Bodhisattvas became popular, spread throughout Central Asia, Korea and Japan, west and south of India.Theravada Buddhism(Older form of Buddhism): south eastwards such as Shri Lanka, Myanmar, Thailand, Indonesia.Dozens of caves for monks located near Western Ghats.
Pilgrims: are men and women who undertake journeys to holy places in order to offer worship.
Chinese Buddhist pilgrims : Fa Xian(1600 yrs ago), Xuan Zang(1400 yrs ago), I-Qing(50yrs after XZ), to visit Buddhist places.
Nalanda(Bihar): Famous Buddhist monastery of the period. Xaun Zang visited Nalanda.
Bhakti (bhaj meaning 'to divide or share' ): A persons' devotion to his/ her chosen diety.Hinduism, Shiva, Vishnu and goddesses such as Durga. Idea of bhakti is present in Bhagavad Gita. Emphasis on devotion and worship of a god/goddess rather than sacrifices.vAppar a devotee of Shiva. Bhakti inspired art : sculpture, poetry and architecture.
Hindu: same history as of 'India' and used to refer to people who lived to the east of the river, to their cultural practices, including religious beliefs.
Christianity: about 2000 yrs ago in West Asia, Jesus Christ born in Bethlehem part of Roman empire. Cristians of Kerala known as Syrian Cristians coz they came from West Asia, amongst the oldest Christian communitines in the world.
-------
New Empires and Kindoms
Guptas dynasty: Samudragupta: Inscription on Ashokan pillar at Allahabad,composed as Kavya by Harishena(poet and minister in the court of Samundragupta).
Prashasti : Sankrit word meaning 'in praise of', for example for Gautamiputra Shri Satakarni, Guptas etc.
Samudragupta's prashasti: warrior: A king who won victories in battle ,learned and best of poets, described as equal to gods, long sentences.Genealogies,Samudragupta's mother Kumara devi: Lichchhavi gana,his father Chandragupta: First ruler of Gupta dynasty, adopted the grand title of maharaj-adhiraja title also used by Samudragupta. Great grandfather and grandfather simply as maha-rajas.
Harishena described four different kind of rulers:
i)Rulers of Aryavarta : Nine rulers uprooted by Samdragupta and kingdom made part of empire. Green color
ii)Rulers of Dakshinapatha : twelve rulers, surrendered to Samdragupta after defeat, allowed to rule again.red dot in the map.
iii) gana sanghas, Assam, coastal Bengal, Nepal: brought tribute, followed his orders, attended his courts. Purple
iv) Rulers of outlying area perhaps descendants of the Kushanas and Shakas, rulers of Sri Lanka: Submitted to him, offered daughters in marriage. Blue
Vikram Samvat : The era beginning in the 58 BCE is traditionally associated with Gupta king,
Chandragupta II, who had founded it as a mark of victory over the Shakas and assumed the title of
Vikramaditya. The Vikram Samvat has also been adopted alongside the Gregorian calendar as the national calendar by independent India. Vikramaditya's court was full of learned people including Kalidasa(poet) & Aryabhata(astronomer).
Kalidasa : Abhijnana Shakuntalam, love story b/w a king Dushyanta & a young woman named Shakuntala.
Harshavardhana and the Harshacharita :
Known about Harshavardhana(king of Thanesar) through his biographies,ruled nearly 1400 yrs ago. Banabhatta was his court poet wrote his biography Harshacharita(genealogy of Harsha + ends with his becoming king) in Sanskrit. Xuan Zang spent a lot of time in Harsha's court. Become king after both his father's and elder brother's death.Brother-in-law was king of Kanauj killed by ruler of Bengal. Harsha took over the kingdom of Kanauj then led an army against the ruler of Bengal, was successful in the east(Magadha & Bengal) but while crossing the Narmada to march into Deccan stopped by Pulakeshin of Chalukya dynasty.
The Pallavas, Chalukyas and Pulakeshin's prashsti: The Pallavas and Chalukyas were the most
important ruling dynasties in south India during this period.
Kingdom of the Pallavas :spread around the capital Kanchipuram to the Kaveri delta.number of assemblies of brahmins land owners called sabha, sabha functions through sub-committees: looked after irrigation, agricultural operations, making roads, local temples etc.
UR: ur was village assembly of non-brahmins.
Nagaram: organisation of merchants.
Kingdom of Chalukyas: capital : Aihole(imp trading centre), centred around the Raichur Doab, b/w rivers Krishna and Tungabhadra. Pulakeshin II : best known Chalukya ruler, known by prashasti composed by his court poet Ravikirti.P-II got the kingdom from his uncle.
Pallavas and Chalukyas frequently attacked each other's kingdom. Ultimately, both dynasty gave way to new rulers of Rashtrakuta and Chola dynasties.
Administration of kingdoms: Village the basic unit of administration, to influence people some imp admin posts were made hereditary. For example, the poet Harishena was maha-danda-nayaka or chief officer, like his father. Many posts to one person, ex Harishena was also kumar-amatya(imp minister) and sandhi-vigrahika(minister of war & peace).local administration like nagara-shreshthi(chief banker), the sarthavaha(leader of merchant caravans).prathama-kulika(chief craftsman), the head of kayasthas(scribes).
New kind of army : Samantas :: no regular salaries but grants of land to collect revenue form, used this to maintain soldiers and horses, equipment for warfare. Banabhatta provide vivid picture of the kings' army.
Arabia: desert, hub of communications for centuries, Arab merchants and sailor played role in sea trade b/w India and Europe. Islam: 1400 yrs ago, introduced by a prophet Muhammad, laid stress on equality and unity of all before Allah: the one supreme god. Quran, withing 100 yrs spread over north Africa, Spain, Iran and India,Arab sailor bought new religion with them, Arab soldier conquered Sind about 1300 yrs ago.
------
The iron pillor : Mehrauli Delhi, made of iron, 7.2 m high, 3 tonnes weighs, made about 1500 yrs ago, inscription on the pillar mention ruler name Chandra(probably Gupta dynasty), not rusted in all these years.
Brick & Stone buildings : stupa :: a mound, round, tall, big & small.small box in the centre of the stupa contains bodily remains(teeth, bones or ashes) of Buddha or his followers or things used by them.Relic casket : covered with earth, later a layer of mud brick or baked brick added on top and then the dome like structure was sometimes covered with carved stone slabs. Pradakshina patha was laid around the stupa, this surrounded with railings, Amaravati: magnificent stupa about 2000 yrs ago. Other buildings were hollowed out of rock to make artificial caves, got painted walls, sculptures.
Hindu Temples : Deities such as Vishnu,Shiva, and Durga, garbhagriha: image of chief deity.sites: In Bhitargaon a tower known as shikharas(requires careful planning), mandapa: for assemblies. Others sites Mahabalipuram and Aihole: Finest stone temples
Painting : Sites : Ajanta:: several caves hollowed out of the hills, monasteries for Buddhist monks decorated with paitings: inside the cave done with in the light of torches, colours(plants & minerals) still vivid even after 1500 yrs.
Epics : grand, local compositions abt heroic men & women, stories abt gods.Tamil epic : Silappadikaram(love story of merchant name Kovalan lived in Puhar fall in love with a courtesen named Madhavi, neglected his wife Kannagi) composed by Ilango(a poet) around 1800 yrs ago. Another one Manimekalai(story of daughter of Kovalan & Madhavi) by Sattanar 1400 yrs ago. Kalidas also wrote epic(Meghaduta). Sanskrit epics the Mahabharata(written down abt 1500 yrs ago but very old, Ved Vyasa) and Ramayana(Valmiki).
Purana(old) : Written Sanskrit verse and for everyone including shudras, stories about god and goddesses such as Vishnu,Shiva,Durga or Parvati, details abt worshipping, account about the creation of the world, stories abt kings.
Jatakas & Panchatantra : Stories abt ordinary people, railings of stupas.
Books on Science : Aryabhatiyam(by mathematician & astronomer Aryabhata), Varahamihira, Brahmagupta and Bhaskaracharya. Invention of Zero, Ayurveda: Charak Samhita(Chraka abt medicine),Susruta Samhita(Sushruta abt surgical procedures)
Paper : In China abt 1900 yrs ago by Cai Lun, kept secret, reached Korea abt 1400 yrs and spread to Japan.from Baghdad(abt 1800 yrs ago) spread to Europe, Africa and other parts of Asia.

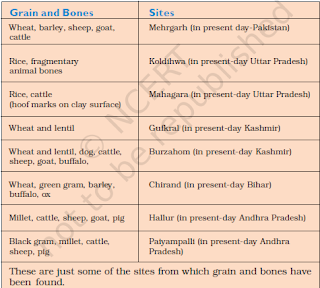




Comments
Post a Comment